Domain names are the lifeblood of every website, they are not just numerical addresses but an integral part of a website’s identity.
However, even the most meticulously managed domain names can slip through your fingers if you’re not vigilant, which can lead to the ordeal that website owners fear: Domain Name Expiry.
We will try to delve deeper into the world of expired domains, drawing on real experiences, to guide you through this complex maze in which you may be an insider.
From understanding the expiration process to extraction and replenishment strategies, we’ll leave no stone unturned.
How does a Domain Name Work?
Before we dive into the abyss of Expired Domains, let’s start by understanding what a domain name is and how a domain name works.
A domain name is like your online identity, or it can be likened to your home address.
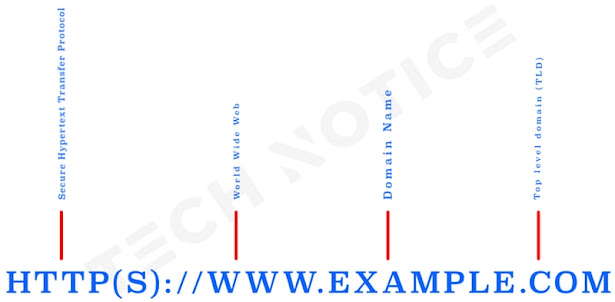
It is what users type in their browsers to access your website. For your information, not every website in the world has a domain with the same name. This is impossible.
A domain name usually consists of two parts: the actual domain name (for example, “my_website”), and the domain extension (for example, “.com”, “.net”, or “.org”).
When you register a new domain, you are essentially renting it for a specific period, typically one year, from the domain registrar, with the possibility of registering the domain for a longer period.
It is a crucial piece of technology for private internet communication, as well as for safeguarding user security and privacy when accessing websites or transferring data.
Here’s why important to use HTTPS for secure browsing:
- Data Encryption: HTTPS uses encryption protocols, typically SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security), to encrypt data exchanged between a user’s web browser and the website’s server.
- Data integrity: HTTPS ensures that data transferred between the user and the website remains unchanged during transmission.
- Authentication: HTTPS also provides authentication, ensuring that users connect to legitimate websites is secure.
- Trust: The presence of a padlock symbol and (https://) in the browser address bar instills confidence in users that their data is safe when interacting with a website.
- SEO and Ranking: Search engines like Google give preference to websites that use HTTPS in their search rankings.
- Compliance: Many regulations and data protection laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), require the use of HTTPS to protect user data.
It is a system of documents and resources that are linked together through hyperlinks and can be accessed over the Internet.
The World Wide Web offers visitors to visit and interact with websites, multimedia content, and other resources using web browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, or Safari.
It has become an essential part of the Internet, enabling people to access information, communicate, and perform various tasks online.
In the context of domain names, a TLD is the highest level in the domain name system hierarchy.
It is the part of a site’s URL that appears at the end of the site address, such as “.com”, “.org”, “.net”, “.gov”, and “.edu”.
TLDs classify and organize domain names on the Internet, and of course each address has a specific purpose for which it can be used.
They are used to indicate the purpose, type, or geographic location of a website or domain.
For example, “.com” is commonly used for commercial websites, “.org” for enterprises, and “.edu” for educational institutions.
Who is The Domain Registrar?
Domain providers are companies or organizations accredited by the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) to provide domain registration services.
They act as intermediaries between domain owners, website owners, and the global Domain Name System (DNS) infrastructure.
Popular registrars include GoDaddy, Namecheap, Google Domains, and Namesilo.
What is the DNS Domain Name?
DNS is the backbone of the Internet.
It’s like an address book that translates human-readable domain names into numeric IP addresses that computers use to identify websites on the web.
Without DNS, we’d be stuck memorizing strings of numbers instead of easy-to-remember domain names.
As a simple example of DNS, all domain names are a series of numbers such as (192.0.2.44) and are converted into a human-understandable format such as (http(s)://www.my_domain.com).
What happens before and after Domain Name Expiry
Domain Age
Domains, unlike physical assets, have a limited lifespan that is defined by a specific period.
When you register a new domain or renew an old domain, it is usually valid for one year, although some registrars offer multi-year registration options.
It is essential to keep track of the expiration date of your domain, as failure to renew it can lead to a series of consequences.
The countdown to Domain Name Expiry
As the expiration date approaches, most registrars will send you multiple email reminders asking to renew the domain.
These notifications act as a great help to end-of-life domain owners, as they remind you to renew your domain before it expires, and ignoring these reminders is where the problems start.
Day of Domain Name Expiry
If you reach the expiration date of your domain, or if the expiration date passes without renewal, your domain will enter a grace period, which is a period during which the domain remains inactive.
This period can vary depending on your domain service provider’s policies, but is usually around 30 days.
During this time, your website becomes down, and visitors are greeted with a frustrating “This site cannot be accessed” message.
The Grace Period for Expire Domain
After the grace period, expired domains usually enter the recovery phase, and this is where things get a little tricky.
Your domain is no longer under your control, and is no longer available for registration, however, you can still get it back by paying an additional (possibly expensive) redemption fee to the registrar.
Expired Domains Marketplace
In some cases, if you fail to redeem your domain in Grace Period for Expire Domain, it may find its way into the expiration auction.
This is a marketplace where anyone can bid on your abandoned domain, the highest bidder will get the rights to the domain, and for you, you will lose all claims to recover it unless you are one of the bidders.
As for how to know expired domains, the best way to reach them is through the expireddomains website, which collects expired and retired domains in one place.
Can I keep my Domain Name Forever?
It’s easy to keep your domain forever, but make sure you do some proactive things, so you don’t get caught up in the spiral of expired domains.
1. Activate the auto-renewal domain feature: Most domain registrars offer the option to activate auto-renewal for domains.
When enabled, your registrar automatically renews your domain for you, usually a few days before your domain expires.
This hands-off approach ensures that renewal deadlines are not missed due to forgetfulness.
Make sure to update your payment information and pay your registration and subscription fees to avoid any hiccups in the automatic renewal process.
2. Enable multi-year registration: Instead of renewing your domain annually, consider registering it for multiple years.
It is a valuable strategy for securing important niches or those with long-term brand potential.
3. Create calendar reminders: In addition to the reminders you get from your domain registrar, set up calendar alerts to notify you when your domain expires.
This extra layer can be a helper for your domain, especially if you manage multiple domains and website at one time.
4. Keep contact information up to date: Make sure the contact information associated with your domain is accurate.
If your email address changes or becomes inactive, you may miss important renewal notifications.
Review and update this information regularly with your registrar.
5. Use domain management tools: Explore domain management tools provided by registrars or third-party services.
These tools often offer advanced features such as bulk scope management, detailed expiration tracking, and comprehensive reporting.
6. Consider domain privacy services: If you’re concerned about privacy, consider using domain privacy or WHOIS protection services.
These can be hide your information in a WHOIS database, making it difficult for scammers to send fack renewal notices.
What do I Do if my Domain Name is Expired?
- Check your email: Make sure you do not miss any renewal notifications from your registrar.
- Renew instantly: If your domain is still in the grace period, renew it immediately through your registrar’s platform.
- Attempt to redeem: If your domain is in the redemption phase, consider your options, pay the fees if your domain is invaluable, or leave it if it’s not worth the cost.
- Monitor Domain Marketplace: Monitor domain expiration auctions, If you are determined to get your domain back, be prepared to offer extra money to get your domain back.
- Choose a reliable domain registrar: Select a reputable domain registrar with a clear policy on domain expiration and redemption.
- Enable auto-renewal: To prevent future incidents, enable auto-renewal for your domains.
- Back up your content: Always keep backups of your website content to avoid data loss.
- Legal Recourse: In rare cases of domain hijacking or wrongful expiration, consult legal counsel for possible recourse.
- Learn from mistakes: Reflect on your experience and make sure you do not repeat it again.
1. Visit the domain registrar’s website: Go to the website of a reputable domain registrar, such as GoDaddy, Namecheap, or Google Domains.
These registrars usually provide tools like Domain Name Search or check domain name tool.
2. Enter the domain name: Find the domain name search or verification tool on the registrar’s home page.
It is usually displayed prominently as a search bar in the center of the page.
Enter the domain name you want to check in the search bar provided, and be sure to include the domain extension (for example, “.com”, “.net”, “.org”).
3. Review the results: Click the “Search” button to start the search, and the registrar’s system will query its database to check the status of the domain you entered.
The search results will provide information about the current status of the field.
Here are common situations you may encounter:
- Domain is active: This means that the domain is currently registered and has not expired.
- Domain name expire: If the domain is listed as expired, it has not been renewed by the previous owner, and it may be available for registration.
- Redemption period: If a domain is in the redemption period, it has recently expired, and the previous owner may still be able to renew it for an additional fee.
- Domain Pending Deletion: This status indicates that the domain is past the redemption period and is about to be released to the public for registration.
4. Check the expiry date: Search results should also show the expiration date of the domain, this date will tell you when the domain expired or when it expired if it is in the redemption period.
5. Consider additional information: Some registrars may provide additional information, such as domain registration history, ownership details, and pricing if the domain is available for purchase.
6. Verification using WHOIS lookup: If you want more detailed information about the domain, you can perform a WHOIS search.
Many domain registrars offer this option. A WHOIS lookup will provide you with information about the domain owner, registration date, and contact details.
Conclusion
Your domain name serves as your online identity, therefore not renewing it might have detrimental effects.
A domain name loss can result in the website your disappearances, even company crises, missed opportunities, and other negative effects.
Actively prevent these possible issues by turning on auto-renewal and regularly checking your email inbox.
You may make sure that your domain is totally in your control by taking a few proactive steps before Domain Name Expiry.